Syntera Marketplace Documentation¶
Introduction¶
Syntera Marketplace is an enterprise-grade platform for deploying, managing, and accessing vector databases, large language models (LLMs), and AI agents on your infrastructure. This documentation provides comprehensive guidance for efficiently utilizing our vector database offerings to power semantic search, recommendations, and other AI-enabled applications.
Table of Contents¶
- Platform Overview
- Available Vector Databases
- Getting Started
- Database Selection Guide
- Database Configuration
- API Reference
- Security & Compliance
- Performance Optimization
- Troubleshooting
- Use Case Examples
- Best Practices
- FAQs
1. Platform Overview¶
Syntera Marketplace enables organizations to deploy and manage high-performance vector databases through a streamlined interface. Our vector database solutions are designed to:
1.1 Key Features¶
- On-Premises Deployment: Run vector databases on your own infrastructure for maximum data security and compliance
- Multi-tenant Capability: Support multiple applications and teams with isolated resources
- Configurable Indices: Optimize for search performance, accuracy, or memory efficiency
- Performance Monitoring: Track query latency, throughput, and resource utilization
- Enterprise Support: Dedicated assistance for deployment and optimization
1.2 Vector Database Architecture¶
The Syntera Vector Database service consists of:
- Model Repository: Curated collection of open-source vector database solutions
- Deployment Engine: Automated system for provisioning databases on your infrastructure
- Management Console: Web interface for configuration and monitoring
- API Gateway: Secure access point for application integration
1.3 System Architecture¶
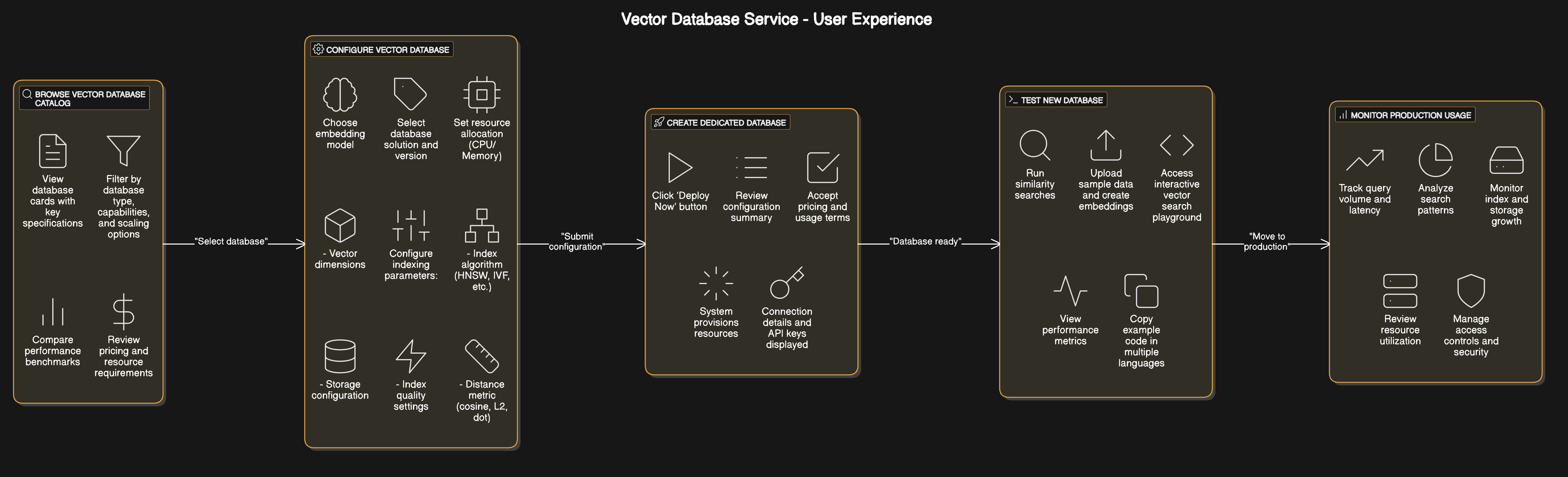
2. Available Vector Databases¶
2.1 Vector Database Options¶
| Database | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chroma DB | Open-source, fast, and scalable vector database | General-purpose vector search, Python applications |
| Milvus | Distributed vector database built on Kubernetes | High-scale production deployments |
| PG Vector | Vector extensions for PostgreSQL | Applications already using PostgreSQL |
| Pinecone DB | Fully-managed vector database service | Real-time, high-performance vector search |
| Qdrant | Vector database with extended filtering capabilities | Complex filtering and hybrid search |
| Weaviate | Semantic vector search engine | Knowledge graph applications |
2.2 Database Comparison¶
| Feature | Chroma DB | Milvus | PG Vector | Pinecone DB | Qdrant | Weaviate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN Algorithms | HNSW, Flat | HNSW, IVF, GPU | HNSW, IVF | HNSW | HNSW | HNSW |
| Metadata Filtering | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ (via SQL) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Storage Options | In-memory, Disk | Distributed | PostgreSQL | Managed | File, Disk | Disk |
| Scaling Model | Vertical | Horizontal | Vertical/Horizontal | Managed | Horizontal | Horizontal |
| License | Apache 2.0 | LGPLv3 | PostgreSQL | Commercial | Apache 2.0 | BSD |
| Best Use Case | Development, Prototyping | Enterprise, High Scale | SQL Integration | Managed Service | Filtering-Heavy | Knowledge Graphs |
2.3 Indexing Algorithms¶
- HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World): Fast approximate search with controllable accuracy
- Flat: Exact search with highest accuracy but slower performance
- IVF (Inverted File Index): Balance between memory usage and search speed
- PQ (Product Quantization): Compression technique for memory efficiency
3. Getting Started¶
3.1 Account Setup¶
- Registration: Create your organization account at marketplace.syntera.ai
- Environment Setup: Configure your infrastructure details
- Authentication: Generate API keys for secure access
3.2 Deploying Your First Vector Database¶
Follow these steps to deploy your first vector database:
- Navigate to the Vector Databases section in the Marketplace dashboard
- Browse and select a database suitable for your use case
- Click "Configure" to set database parameters
- Deploy the database to your infrastructure
- Retrieve connection details (endpoint URL, API key, credentials)
- Test connectivity using the built-in playground
- Integrate the API endpoint into your application
3.3 Basic Operations Workflow¶
A typical vector database workflow includes:
- Convert Data to Embeddings: Transform text, images, or other data into vector embeddings
- Store Vectors: Add vectors and associated metadata to your database
- Create Indices: Build optimized indices for fast similarity search
- Query for Similarity: Search for similar vectors based on distance metrics
- Filter Results: Apply metadata filters to narrow down search results
4. Database Selection Guide¶
4.1 Evaluation Criteria¶
Consider these factors when selecting a vector database:
- Scale Requirements: Expected vector count and query volume
- Query Latency Needs: Importance of low-latency responses
- Accuracy Requirements: Tolerance for approximate results
- Filtering Capabilities: Need for complex metadata filtering
- Integration Needs: Compatibility with existing tech stack
- Resource Constraints: Available infrastructure capacity
4.2 Use Case Matching¶
| Use Case | Recommended Databases | Important Features |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic Search | Chroma DB, Weaviate | Hybrid search, text preprocessing |
| Recommendation Systems | Milvus, Pinecone DB | High throughput, real-time updates |
| Image Similarity | Qdrant, Milvus | Multi-modal support, filtering |
| Document Retrieval | Chroma DB, PG Vector | Text chunking, metadata storage |
| Anomaly Detection | Qdrant, Pinecone DB | Fast indexing, distance metrics |
| Multi-tenant Applications | Milvus, Weaviate | Collection isolation, access control |
4.3 Hardware Considerations¶
Different databases have varying hardware requirements:
- Memory-Optimized: For in-memory databases like Chroma (in-memory mode)
- Storage-Optimized: For disk-based databases with large vector collections
- CPU-Intensive: For high query throughput requirements
- GPU-Accelerated: For databases supporting GPU acceleration (e.g., Milvus)
5. Database Configuration¶
5.1 Basic Configuration¶
5.1.1 Database Information¶
- Instance Name: Identifier for your deployed database
- Database Type: Selected vector database solution (e.g., Chroma DB, Milvus)
5.1.2 Embedding Settings¶
| Parameter | Type | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embedding Model | Selection | Model used to generate vectors | Dimensionality, domain compatibility |
| Embedding Dimension | Integer | Size of vector embeddings | Higher dimensions = better accuracy, more resources |
| Batch Size | Integer | Records processed together | Higher = faster ingestion, more memory |
| Max Sequence Length | Integer | Token limit for text inputs | Higher = more context, slower processing |
5.2 Indexing Configuration¶
5.2.1 Indexing Strategy¶
| Parameter | Type | Description | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Index Type | Selection | Algorithm for similarity search | Speed vs. accuracy vs. memory |
| HNSW M Parameter | Integer | Graph connectivity in HNSW | Higher = better recall, more memory |
| EF Construction | Integer | Search quality during build | Higher = better quality, slower builds |
| Vector Space | Selection | Distance metric (cosine, L2, dot) | Depends on embedding properties |
5.2.2 Collection Settings¶
- Default Collection: Name for the primary vector collection
- Embedding Function: Method for converting data to vectors
- Metadata Configuration: Schema for additional attributes
5.3 Infrastructure Configuration¶
- CPU Allocation: Processing power for query handling
- Memory Allocation: RAM for index and cache storage
- Storage Settings: Persistence configuration for vectors
- Scaling Options: Configuration for handling growth
6. API Reference¶
6.1 Authentication¶
All API requests require authentication:
curl -X POST "https://your-db-instance.chroma.ai/api/v1/collections/my_collection/query" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query_embeddings": [[0.1, 0.2, ...]]
}'
6.2 Common Endpoints¶
6.2.1 Collections Management¶
Create a new collection:
List collections:
Delete a collection:
6.2.2 Vector Operations¶
Add vectors:
{
"ids": ["id1", "id2"],
"embeddings": [[0.1, 0.2, ...], [0.3, 0.4, ...]],
"documents": ["text document 1", "text document 2"],
"metadatas": [
{"category": "electronics", "price": 99.99},
{"category": "books", "price": 12.99}
]
}
Query vectors:
{
"query_embeddings": [[0.1, 0.2, ...]],
"n_results": 5,
"where": {"category": "electronics"},
"include": ["documents", "metadatas", "distances"]
}
6.3 Database-Specific APIs¶
Different vector databases may have additional specialized endpoints:
Chroma DB¶
Qdrant¶
{
"vector": [0.1, 0.2, ...],
"limit": 10,
"filter": {
"must": [
{"key": "category", "match": {"value": "electronics"}}
]
}
}
6.4 Response Format¶
6.4.1 Query Response¶
{
"ids": [["id5", "id1", "id8"]],
"distances": [[0.12, 0.28, 0.35]],
"documents": [["document text 5", "document text 1", "document text 8"]],
"metadatas": [[
{"category": "electronics", "price": 199.99},
{"category": "electronics", "price": 99.99},
{"category": "electronics", "price": 149.99}
]]
}
6.4.2 Error Response¶
{
"error": {
"code": 400,
"message": "Invalid request: missing required parameter 'embeddings'",
"type": "invalid_request_error",
"param": "embeddings"
}
}
7. Security & Compliance¶
7.1 Data Protection¶
- Data Isolation: All vector data remains within your infrastructure
- Encryption at Rest: Configure storage encryption for sensitive vector data
- Encryption in Transit: TLS for all API communications
- Data Backup: Scheduled backups of vector collections and metadata
7.2 Access Control¶
- API Key Management: Create, rotate, and revoke access credentials
- Role-Based Access: Configure permissions for different users/services
- Collection-Level Permissions: Restrict access to specific vector collections
- IP Restrictions: Limit API access to trusted networks
7.3 Compliance Features¶
- Audit Logging: Track all operations for compliance requirements
- GDPR Support: Features to help meet data protection regulations
- Data Deletion: Purge vectors and associated metadata on request
- PII Handling: Best practices for personally identifiable information
8. Performance Optimization¶
8.1 Index Optimization¶
| Algorithm | Parameter | Effect | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| HNSW | M | Controls graph connectivity | 12-48 (higher for better accuracy) |
| HNSW | ef_construction | Search quality during build | 100-500 (higher for better index) |
| HNSW | ef_search | Search quality at query time | 50-500 (higher for better recall) |
| IVF | nlist | Number of clusters | sqrt(vector_count) to 4*sqrt(vector_count) |
| IVF | nprobe | Clusters to search | 1-10% of nlist value |
8.2 Resource Allocation Guidelines¶
| Vector Count | Dimensions | Recommended RAM | CPU | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100K | 768 | 4 GB | 2 cores | 10 GB SSD |
| 100K - 1M | 768 | 8-16 GB | 4 cores | 50 GB SSD |
| 1M - 10M | 768 | 32-64 GB | 8 cores | 200 GB SSD |
| 10M - 100M | 768 | 128+ GB | 16+ cores | 1+ TB SSD |
8.3 Query Optimization¶
- Vector Caching: Enable caching for frequently accessed vectors
- Batch Processing: Group similar requests to reduce overhead
- Asynchronous Operations: Use non-blocking queries for high-throughput scenarios
- Metadata Indexing: Create indices on frequently filtered metadata fields
- Query Planning: Structure complex queries for optimal execution
8.4 Scaling Strategies¶
- Vertical Scaling: Increase resources (memory, CPU) for single-node deployments
- Horizontal Scaling: Add nodes for distributed databases (Milvus, Qdrant, Weaviate)
- Sharding: Distribute collections across multiple shards
- Replication: Create read replicas for higher throughput
- Load Balancing: Distribute queries across available resources
9. Troubleshooting¶
9.1 Common Issues¶
| Issue | Possible Causes | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| High Query Latency | Insufficient resources, unoptimized index | Increase resources, optimize index parameters |
| Poor Search Quality | Inappropriate algorithm, low ef_search | Adjust search parameters, switch index type |
| Out of Memory Errors | Index too large for RAM | Increase memory, switch to disk-based storage |
| Slow Indexing | High dimensionality, strict parameters | Adjust batch size, relax index quality parameters |
| Connection Failures | Network issues, authentication problems | Check firewall rules, verify credentials |
9.2 Diagnostic Tools¶
- Health Check API: Verify service status and component health
- Metrics Dashboard: Monitor performance and resource utilization
- Query Profiler: Analyze slow queries to identify bottlenecks
- Log Analysis: Review logs for errors and warning patterns
- Connection Tester: Validate network connectivity and authentication
9.3 Common Error Codes¶
| Error Code | Description | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | Check request format and parameters |
| 401 | Unauthorized | Verify API credentials |
| 404 | Not Found | Confirm collection/endpoint exists |
| 413 | Payload Too Large | Reduce batch size or vector dimension |
| 429 | Too Many Requests | Implement rate limiting or increase quota |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | Check resource utilization and service status |
10. Use Case Examples¶
10.1 Semantic Search¶
import chromadb
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# Connect to your Syntera-deployed Chroma instance
client = chromadb.Client(
endpoint="https://your-db-instance.chroma.ai",
api_key="your-api-key"
)
# Initialize or get collection
collection = client.get_or_create_collection("product_search")
# Load embedding model
model = SentenceTransformer('sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# Add product descriptions
product_texts = [
"Wireless ergonomic keyboard with RGB backlight",
"Ultra-thin laptop with 16-hour battery life",
"Noise-cancelling bluetooth headphones"
]
product_ids = ["product-1", "product-2", "product-3"]
product_embeddings = model.encode(product_texts).tolist()
product_metadata = [
{"category": "accessories", "price": 79.99},
{"category": "computers", "price": 1299.99},
{"category": "audio", "price": 249.99}
]
collection.add(
embeddings=product_embeddings,
documents=product_texts,
metadatas=product_metadata,
ids=product_ids
)
# Search for products
query = "wireless keyboard for gaming"
query_embedding = model.encode([query]).tolist()
results = collection.query(
query_embeddings=query_embedding,
n_results=2,
include=["documents", "metadatas", "distances"]
)
print("Search results for:", query)
for i, (doc, metadata, distance) in enumerate(zip(
results['documents'][0],
results['metadatas'][0],
results['distances'][0]
)):
print(f"{i+1}. {doc} (Score: {1-distance:.2f})")
print(f" Category: {metadata['category']}, Price: ${metadata['price']}")
10.2 Recommendation System¶
import numpy as np
import requests
import json
API_URL = "https://your-db-instance.qdrant.ai"
API_KEY = "your-api-key"
COLLECTION = "product_recommendations"
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}"
}
# Function to get user embeddings based on behavior
def get_user_embedding(user_id):
# In a real system, this would be generated from user behavior
# For this example, we create a random embedding
return np.random.rand(768).tolist()
# Get similar products based on user preferences
def get_recommendations(user_embedding, category=None, limit=5):
query_data = {
"vector": user_embedding,
"limit": limit
}
# Add category filter if specified
if category:
query_data["filter"] = {
"must": [
{"key": "category", "match": {"value": category}}
]
}
response = requests.post(
f"{API_URL}/collections/{COLLECTION}/points/search",
headers=headers,
data=json.dumps(query_data)
)
return response.json()
# Get recommendations for user
user_id = "user-123"
user_embedding = get_user_embedding(user_id)
recommendations = get_recommendations(user_embedding, category="electronics")
print(f"Recommended products for user {user_id}:")
for i, result in enumerate(recommendations.get('result', [])):
product = result['payload']
score = result['score']
print(f"{i+1}. {product['name']} (Score: {score:.2f})")
print(f" Price: ${product['price']}, Category: {product['category']}")
10.3 Document Retrieval for LLM Context¶
import requests
import json
from langchain.vectorstores import PGVector
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Connect to your PG Vector instance
CONNECTION_STRING = "postgresql+psycopg2://user:[email protected]:5432/vectordb"
COLLECTION_NAME = "document_store"
# Load and split document
loader = TextLoader("company_handbook.txt")
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# Initialize embedding model
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
# Store documents in vector database
db = PGVector.from_documents(
documents=texts,
embedding=embeddings,
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
connection_string=CONNECTION_STRING
)
# Create retrieval-based QA chain
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=OpenAI(),
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=retriever
)
# Ask questions using retrieved context
query = "What is our company's work from home policy?"
result = qa_chain.run(query)
print(f"Question: {query}")
print(f"Answer: {result}")
11. Best Practices¶
11.1 Data Preparation¶
- Normalize Input Data: Clean and standardize text before embedding
- Chunking Strategy: Find optimal document chunk size for your use case
- Embedding Selection: Choose domain-appropriate embedding models
- Quality Control: Filter out low-quality or duplicate vectors
- Metadata Design: Plan metadata schema for efficient filtering
11.2 Index Configuration¶
| Database | Parameter | Recommendation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chroma DB | hnsw:M | 16 for < 1M vectors, 32 for > 1M | Higher values improve recall at cost of memory |
| Milvus | nlist | sqrt(N) where N is vector count | Balance between search speed and accuracy |
| Qdrant | ef_construction | 128 for quality, 64 for speed | Affects index build time and quality |
| All | Batch Size | 10,000 for bulk operations | Adjust based on memory constraints |
11.3 Production Deployment¶
- Staging Environment: Test configuration in staging before production
- Resource Monitoring: Set up alerts for high utilization
- Backup Strategy: Regular backups with versioning
- Scaling Plan: Define triggers and process for scaling resources
- High Availability: Configure replication for critical applications
11.4 Query Optimization¶
- Use Filtering: Apply metadata filters to reduce search space
- Right-Size Results: Request only needed number of results (n_results)
- Batch Similar Queries: Combine related searches when possible
- Include Only Needed Data: Specify fields to return with "include" parameter
- Monitor Slow Queries: Create logs for queries exceeding latency thresholds
12. FAQs¶
12.1 General Questions¶
Q: What's the difference between exact and approximate nearest neighbors search?
A: Exact search guarantees finding the closest vectors but can be slow for large datasets. Approximate methods like HNSW trade perfect accuracy for dramatically improved speed, making them practical for production use with millions of vectors.
Q: How many vectors can a single vector database instance handle?
A: This depends on the specific database, available resources, and configuration. With proper resources, Milvus and Qdrant can handle hundreds of millions of vectors, while Chroma DB and PG Vector typically perform best with tens of millions of vectors per instance.
Q: Can I use different embedding models with the same vector database?
A: Yes, but vectors from different models should be stored in separate collections as their dimensionality and semantic spaces may differ, making cross-model similarity search meaningless.
12.2 Technical Questions¶
Q: What distance metric should I use for my embeddings?
A: Common choices are cosine similarity for normalized embeddings (most text embeddings), Euclidean (L2) for spatial data, and dot product for some specialized cases. Match the metric to your embedding model's recommendations.
Q: How can I improve search accuracy?
A: Increase the ef_search parameter for HNSW indices, use higher quality embedding models, implement hybrid search combining vector and keyword search, and ensure proper data preprocessing.
Q: How do I handle document updates?
A: Most vector databases support upsert operations where you can update vectors and metadata using the same ID. Some databases (like Chroma) may require deleting and re-adding the vector if the embedding itself changes.
Q: What's the best way to handle very large documents?
A: Split documents into semantically meaningful chunks (paragraphs, sections) of 512-1024 tokens, create embeddings for each chunk, and store with metadata linking back to the source document. This improves retrieval precision.
12.3 Operational Questions¶
Q: How often should I rebuild indices?
A: For most vector databases, indices are updated incrementally as you add data. Complete rebuilds are rarely needed unless you change fundamental index parameters or experience fragmentation issues after many updates/deletes.
Q: What's the expected query latency?
A: With proper configuration, most vector databases can deliver sub-100ms query times for collections of millions of vectors. Latency increases with collection size, dimensionality, and desired recall accuracy.
Q: How do I monitor vector database health?
A: Monitor system metrics (CPU, memory, disk I/O), database-specific metrics (query latency, index size), and application-level metrics (recall accuracy on known datasets).
Last updated: May 11, 2025